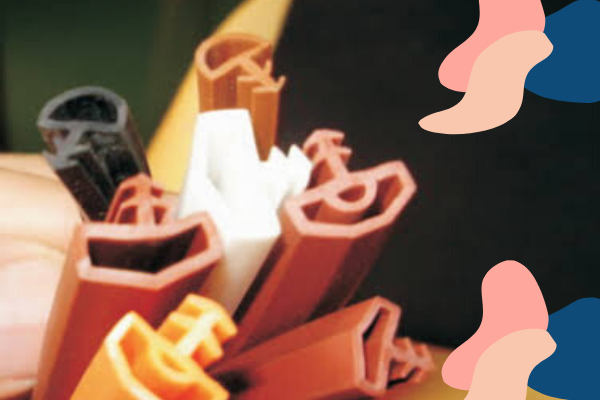
EPDM – What does EPDM MEAN?
EPDM is very versatile. The words EPDM stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer. It is a kind of synthetic rubber. EPDM is applied in numerous applications. It is even a Engineering Product Data Management and is very prominently used in the automotive and structure industries. This synthetic rubber is normally used for window, door seals, waterproofing sheets as well as electrical gaskets. EPDM rubber is a multipurpose synthetic material usually even used for insulation and sealing. EPDM is used in compression and joints seals in pipe products that exist in trenchless construction. It could even be used as part of a trenchless reintegration solution.
EPDM is highly preferred as a material among engineers for its unbeatable features. The preferred characteristic of EPDM is that they are versatile and can be used in many ways based on the industrial requirement. EPDM roofing membrane is one of the most common choices on the market nowadays. For this reason, numerous people are fairly attentive to know the benefits of this products, particularly compared with the other.
As with all building materials, it has its own pros and cons, and it is eventually how these pros and cons affect your specific project that make one of them the perfect choice. Here are few of the reasons why you must choose EPDM.
- Synthetic rubber EPDM gives excellent all-round excellent surviving resistance and performance, this is due to it having a very inert chemical properties.
- As compare to other materials, such products will both wear down the period of time, nonetheless the extent of this all relies on the conditions that the material is placed in and superiority of the product and its connection.
- EPDM roofing sheath is called for being a very resistant product, and can bear all kinds of weather conditions. This is valuable in all types of climates, such as hot and quite cold ones, and those with flexible weather conditions all through the year. Extravagances of temperature do not touch this product at all.
Applications suitable for EPDM:
EPDM rubber is applied in seals, glass-run channels, o-rings, radiators, appliance hose, garden and tubing, washers, belts, pond liners, solar panel heat collectors, electrical insulation, and speaker cone surrounds. It is even used as a intermediate for water resistance in electrical cable-jointing, geomembranes, roofing membranes, plastic impact modification, rubber mechanical goods, thermoplastic, vulcanizates, and numerous additional applications. These EPDM profiles India are available in different sizes, dimensions and grades.
When is EPDM rubber the correct choice for insulation and sealing?
EPDM gaskets and seals is applied extensively with equipment and vehicles, nonetheless this synthetic elastomer has inacceptable resistance to diesel fuel, gasoline, and motor oil. EPDM’s benefits are various, however, and this cost-effective multifarious is usually a better selection than silicones especially when it comes to outdoor environments. Industry specialists in roofing, automotive, and other applications use EPDM sheet rubber to produce mechanisms that can function and last through out-of-doors situations. It is the tried-and-true elastomer for weathering. Though, it requests the question: what makes the EPDM elastomer so resilient to surviving from UV rays and ozone? The answer lies in the rubber’s chemical configuration. It is produced from the sun and additional sources such as black lights. Ozone is a molecule obviously look as a gas in the Earth’s atmosphere. Upon contact with a material, both ozone and UV attack any susceptible chemical bonds in the material’s chemical backbone. This changes the molecular structure of said material. When the material’s chemical backbone is adapted or interfered with in any method, degradation will happen. EPDM rubber also offers good-to-high tensile elasticity and strength. Tensile strength, the resistance of a material to breaking below tension.
The vital features of EPDM are as follows:
- In EPDM the content of ethylene is between 50 to 75 per cent
- The occurrence of larger ethylene content permits the higher possibility for loading polymer, improved mixing and extrusion.
- The formless polymer is best for dispensation
- EPDM is greatly motivated by their molecular structure
- The dye present in EPDM classically has of 2.5 wt% and up to 12wt% of the composition serves when curing with sulphur and resin. When dyne is cured with peroxide it acts as a cogent that provides resistance to unwanted tackiness or flows during usage.
- In comparison with their amorphous counterpart peroxide curing of polymer offers EPDM advanced cross-linking density.
- EPDM is generally used instead of silicones, nitrile, or thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs). Silicones can survive larger and lesser both temperatures.
- Outstanding resistant to weathering
- Flame resistant
- Stability associated to other rubber products
- Most hard-wearing
- used for almost application that require durable
- Custom Design for all type of Rubber Products